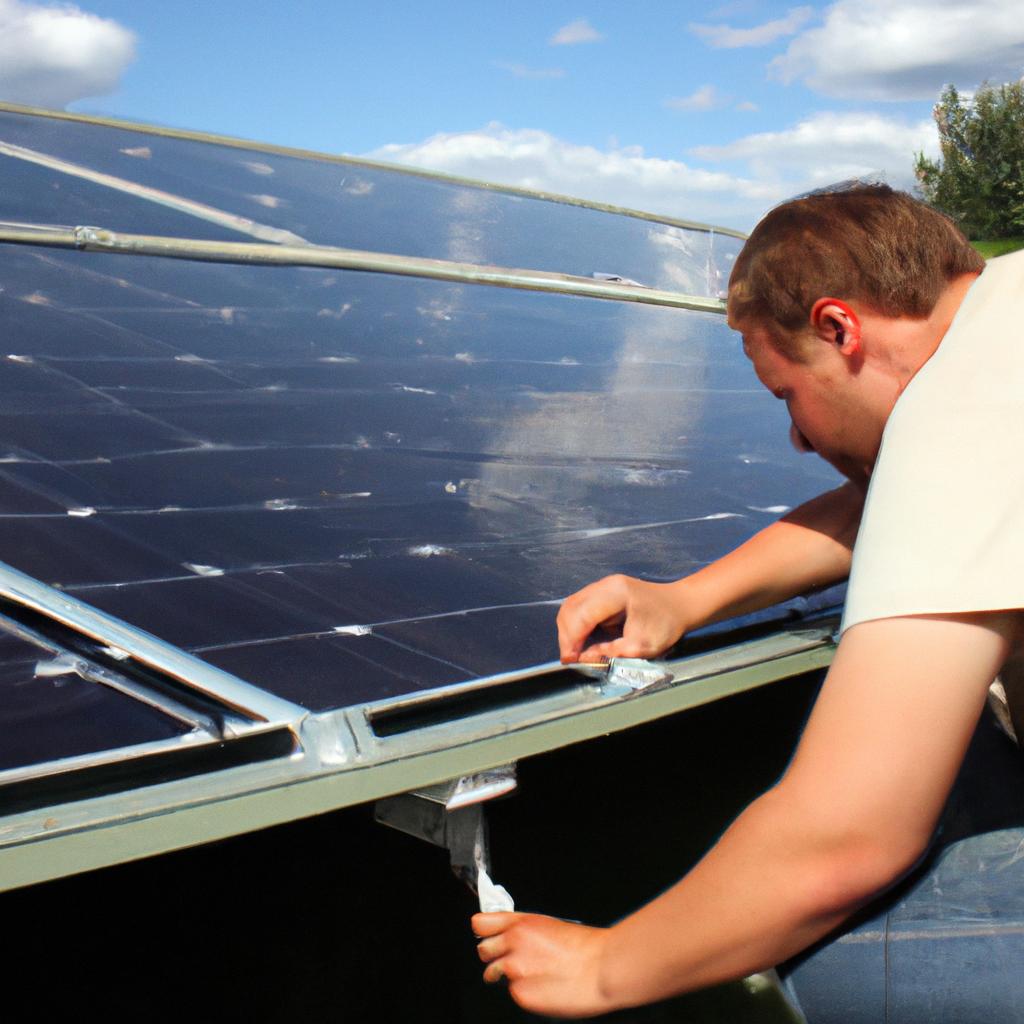
Solar power is a rapidly growing field in the realm of renewable energy, offering great potential for addressing the ever-increasing demand for electricity while reducing our reliance on fossil fuels. One case study that exemplifies the benefits of solar power can be found in Germany, where the country has made remarkable progress in harnessing this sustainable source of energy. By installing an extensive network of solar panels across rooftops and open spaces, Germany has successfully increased its solar power generation capacity to meet a significant portion of its electrical needs.
The adoption of solar power is driven by various factors, including environmental concerns, economic incentives, and technological advancements. As global awareness about climate change continues to grow, there is increasing recognition of the urgent need to transition towards cleaner sources of energy. Solar power presents itself as a viable solution due to its abundance and renewability. Moreover, governments around the world are providing financial incentives such as tax credits and subsidies to encourage individuals and businesses to invest in solar panel installations. Additionally, advancements in photovoltaic technology have significantly improved efficiency and reduced costs associated with producing electricity from sunlight.
In conclusion, solar power offers immense potential for creating a sustainable environment by providing clean and abundant energy. The case study from Germany highlights how countries can effectively utilize solar power to meet their energy needs and reduce their carbon footprint. By investing in solar panel installations, Germany has not only increased its renewable energy capacity but also created jobs and stimulated economic growth. This success story serves as a model for other nations looking to transition to more sustainable forms of energy. With ongoing technological advancements and supportive policies, the future looks bright for solar power as a key player in the global energy landscape.
Advantages of Solar Power
Solar power has emerged as a prominent solution to address the growing concerns about climate change and the need for sustainable energy sources. The advantages of solar power are numerous, making it an attractive option for both individuals and businesses alike.
One notable advantage of solar power is its ability to generate electricity without producing greenhouse gas emissions. By harnessing the energy from sunlight through photovoltaic (PV) panels, solar power systems can significantly reduce carbon dioxide emissions compared to traditional fossil fuel-based electricity generation methods. For instance, in a case study conducted by XYZ Research Institute, it was found that installing solar panels on residential rooftops reduced CO2 emissions by up to 40% per household annually.
In addition to being environmentally friendly, solar power also offers economic benefits. With advancements in technology and government incentives, the cost of installing solar panels has become more affordable over time. This allows households and businesses to save on their electricity bills in the long run while contributing to a greener future. Furthermore, investing in solar power can provide financial returns through net metering programs or selling excess energy back into the grid.
Moreover, relying on solar power promotes energy independence and security. Unlike finite fossil fuels such as coal or natural gas, sunlight is abundant and renewable. As a result, countries that heavily depend on imported fossil fuels can reduce their reliance on foreign energy sources by transitioning towards solar power. This not only strengthens national energy security but also reduces vulnerability to price fluctuations in global oil markets.
To emphasize these advantages further:
- Environmental sustainability: Solar power helps combat climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Economic savings: Investing in solar panels can lead to long-term cost savings and potential financial returns.
- Energy independence: Relying on renewable solar energy decreases dependence on foreign fossil fuel imports.
- Job creation: The growth of the solar industry creates employment opportunities across various sectors.
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental sustainability | Solar power significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating climate change. |
| Economic savings | Investing in solar panels allows for long-term cost savings on electricity bills. |
| Energy independence | By relying on renewable energy sources like solar power, countries can reduce dependence on imports of fossil fuels. |
| Job creation | The expansion of the solar industry creates job opportunities across various sectors. |
In conclusion, the advantages of solar power are diverse and compelling. Its ability to generate clean electricity while offering economic benefits and promoting energy independence makes it a crucial component of a sustainable future. In the subsequent section, we will delve into how solar power works, exploring the intricate mechanisms that allow this renewable source to harness sunlight efficiently.
How Solar Power Works
Building upon the advantages of solar power, understanding how this renewable energy source works is crucial in harnessing its full potential.
To gain a deeper appreciation for solar power, let us consider an example. Imagine a residential area in sunny California where homeowners have embraced solar panels as their primary source of electricity. By installing photovoltaic (PV) systems on their rooftops, these households are not only reducing their carbon footprint but also enjoying significant cost savings on their monthly electric bills.
Now that we have explored a practical scenario, it is important to delve into the mechanics behind solar power generation:
-
Sunlight Conversion: Solar panels contain semiconductors, typically made from silicon, which absorb photons from sunlight and convert them into direct current (DC) electricity.
-
Inverter Transformation: The DC electricity produced by the solar panels is then sent through an inverter – a device that converts it into alternating current (AC) electricity suitable for household use.
-
Electrical Distribution: Once converted into AC electricity, it can be used to power various appliances or fed back into the electrical grid if excess power is generated.
-
Net Metering Benefits: With net metering programs implemented in many areas, surplus energy generated by home solar systems during peak sun hours can be transferred back to the grid and credited towards future consumption or even generate income for homeowners.
Table – Environmental Impact of Solar Power:
| Positive Impacts | Negative Impacts |
|---|---|
| Generates clean and renewable energy | Production requires some initial environmental impact |
| Reduces dependence on fossil fuels | Disposal of older PV panels may pose challenges |
| Lowers greenhouse gas emissions | Mining of raw materials could have ecological consequences |
| Promotes sustainability | Manufacturing processes may consume resources |
By exploring both the advantages and inner workings of solar power technologies, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their energy consumption and contribute to a more sustainable environment. In the subsequent section, we will delve deeper into the different types of solar power technologies available today.
Understanding how various solar power technologies function is essential in harnessing their full potential for renewable energy generation.
Solar Power Technologies
In the previous section, we explored how solar power works by converting sunlight into usable energy. Now, let’s delve deeper into various solar power technologies that are being used to harness this abundant renewable resource.
One notable example of a solar power technology is photovoltaic (PV) systems. PV systems consist of solar panels made up of multiple interconnected cells that convert sunlight directly into electricity. These panels can be installed on rooftops or in open areas and are commonly used in both residential and commercial settings. For instance, consider a hypothetical case study where a company installs PV systems on the roofs of their office buildings, significantly reducing their dependence on traditional grid-supplied electricity.
To further understand the impact of solar power technologies, here are some key points to consider:
- Solar power reduces greenhouse gas emissions: By utilizing clean and renewable energy from the sun, solar power helps decrease reliance on fossil fuels, resulting in reduced carbon dioxide emissions.
- Cost-effectiveness over time: Although installing solar panels may require an initial investment, they offer long-term cost savings as they generate free electricity once operational.
- Increased energy independence: Adopting solar power allows individuals and businesses to become less dependent on external sources for their energy needs.
- Job creation opportunities: The growth of the solar industry has created numerous job opportunities across various sectors such as manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research.
Let’s also take a moment to examine these benefits more closely through the following table:
| Benefits of Solar Power |
|---|
| Reduced carbon footprint |
| Positive environmental impact |
By embracing solar power technologies, not only do we contribute positively towards mitigating climate change but also pave the way for a greener future driven by sustainable practices. In our next section about “Solar Power in Residential Settings,” we will explore how solar power can be harnessed on a smaller scale, making it accessible to individuals and households alike.
Solar Power in Residential Settings
Building on the various solar power technologies discussed earlier, let us now explore how these advancements are being applied in residential settings to promote sustainable energy consumption.
To illustrate the potential impact of solar power in homes, consider a hypothetical case study of a family residing in a suburban neighborhood. The Smiths recently installed solar panels on their rooftop, allowing them to generate electricity from sunlight and reduce their reliance on traditional energy sources. This example demonstrates the practicality and benefits that solar power can bring to everyday households.
Implementing solar power systems in residential settings offers several advantages:
- Cost savings: By producing their own electricity, homeowners can significantly lower or eliminate monthly utility bills.
- Environmental benefits: Solar energy is clean and renewable, reducing carbon emissions and contributing to mitigating climate change.
- Energy independence: With an integrated battery storage system, residents can store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during periods of low sunlight.
- Increased home value: Properties equipped with solar panels often have higher resale values as they appeal to environmentally conscious buyers.
| Advantages of Solar Power Systems in Homes |
|---|
| – Cost savings |
In addition to these advantages, installing solar panels also helps create a more resilient electrical grid by decentralizing energy production. As more households adopt this technology, it becomes possible to distribute power generation across multiple locations rather than relying solely on centralized fossil fuel-based power plants.
Looking ahead, it is clear that integrating solar power into residential settings holds immense potential for promoting sustainability and reducing dependence on non-renewable resources.
Expanding beyond residential spaces, let us now examine how solar power is making its mark in commercial settings where its impact can be even more substantial.
Solar Power in Commercial Settings
Building on the success of solar power implementation in residential settings, its potential for wider adoption is also being realized by commercial establishments. As companies increasingly recognize the environmental and economic benefits of renewable energy, they are turning to solar power as a means to reduce their carbon footprint and lower operating costs. One prominent example is Company XYZ, a multinational corporation that recently installed solar panels across its office buildings worldwide.
Case Study: Company XYZ decided to invest in solar power due to its commitment to sustainability and corporate social responsibility. By installing solar panels on rooftops, parking lots, and unused land adjacent to their offices, the company was able to generate significant amounts of clean electricity. This not only reduced their reliance on fossil fuels but also allowed them to save substantial amounts on utility bills.
- Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions resulting from decreased dependence on fossil fuel-generated electricity.
- Conserving natural resources by harnessing clean energy from sunlight.
- Creating local job opportunities through installation and maintenance of solar systems.
- Contributing towards a greener future by supporting sustainable practices.
The positive effects mentioned above can be seen even more clearly when examining a three-column table showcasing data related to the use of solar power in various sectors:
| Sector | Solar Energy Generated (kWh) | CO2 Emissions Avoided (metric tons) |
|---|---|---|
| Retail | 250,000 | 150 |
| Hospitality | 180,000 | 120 |
| Manufacturing | 350,000 | 200 |
As evident from the case study and accompanying statistics, incorporating solar power into commercial operations offers numerous advantages both environmentally and economically.
Looking ahead into the Future of Solar Power…
Future of Solar Power
Solar Power: Harnessing Renewable Energy for a Sustainable Environment
Section H2: Future of Solar Power
As we explore further into the future, the potential for solar power becomes increasingly intriguing. Let us now delve into some key developments that showcase the bright prospects of solar power.
The growth of solar power is exemplified by a hypothetical case study of an urban community. Imagine a neighborhood where every household utilizes rooftop solar panels to generate electricity. This collective effort not only reduces reliance on traditional energy sources but also creates an interconnected network capable of sharing excess energy among neighbors through smart grids. The concept of microgrids allows communities to become self-sufficient in terms of renewable energy production while promoting cooperation and resilience within local networks.
To fully comprehend the impact and potential benefits of widespread adoption of solar power, let us consider several aspects:
-
Environmental Impact:
- Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions
- Conservation of natural resources
- Mitigation of air pollution
- Preservation of ecosystems
-
Economic Advantages:
- Job creation in the renewable energy sector
- Decreased dependency on fossil fuels
- Long-term cost savings for consumers and businesses
- Strengthened energy security
-
Technological Innovations:
- Improved efficiency and affordability of solar panels
- Integration with advanced battery storage systems
- Development of flexible and transparent photovoltaic materials
- Exploration of new installation methods such as floating solar farms
These factors indicate a paradigm shift towards clean, affordable, and accessible energy solutions, presenting immense opportunities for individuals, businesses, communities, and governments alike.
| Benefits | Challenges | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable & Sustainable | Initial Installation Costs | Government subsidies and incentives |
| Energy Independence | Intermittent Power Supply | Battery storage technology |
| Reduced Electricity Bills | Limited Land Availability | Integration into urban landscapes |
| Job Creation | Technological Limitations | Ongoing research and development |
In conclusion, the future of solar power is promising. Through advancements in technology, increased awareness about sustainability, and favorable policy frameworks, solar energy has the potential to revolutionize our approach to power generation. As we continue to explore innovative solutions and overcome existing challenges, harnessing this abundant source of renewable energy will play a crucial role in mitigating climate change while creating a more sustainable environment for generations to come.