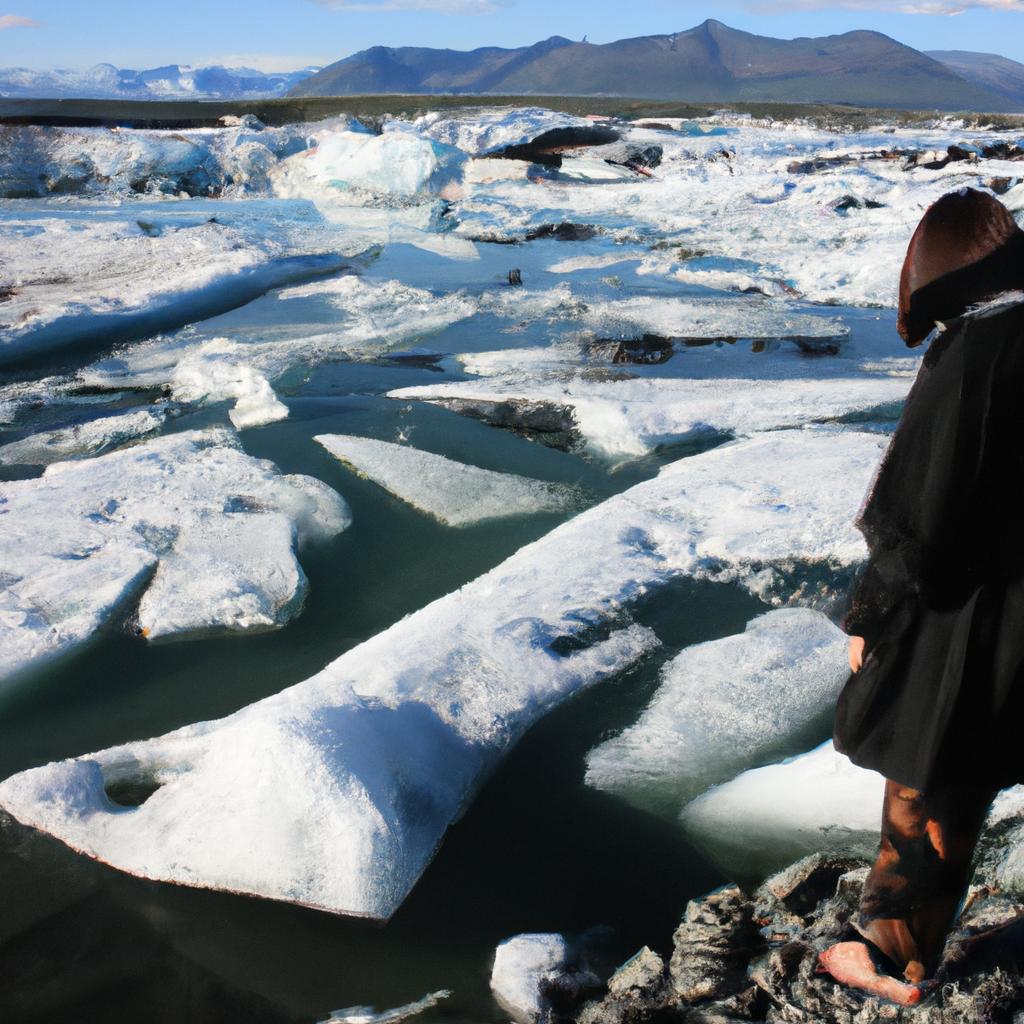
Climate change is a ubiquitous phenomenon that has become a subject of concern in recent years due to its detrimental impact on the environment. The intricate interplay between climate patterns and the delicate balance of ecosystems makes this issue particularly complex. For instance, consider the hypothetical case study of a coastal city experiencing rising sea levels as a result of global warming. This scenario highlights how climate change can disrupt not only natural habitats but also human settlements, posing significant challenges for policymakers and scientists alike.
The consequences of climate change extend far beyond the boundaries of individual cities or regions. From melting ice caps to extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and droughts, various manifestations of this environmental crisis have emerged worldwide. These changes bring about severe ecological disruptions, including altered biodiversity patterns, reduced crop yields, and the displacement of numerous species from their natural habitats. Consequently, understanding the multifaceted impacts of climate change becomes crucial in order to develop effective mitigation strategies and adapt to an increasingly uncertain future.
In light of these complexities, this article aims to delve deeper into the repercussions posed by climate change on our environment. By examining both local and global case studies, we will explore how different factors like temperature variations, precipitation shifts, and rising sea levels contribute to ecosystem disturbances. Furthermore, we will discuss the potential solutions and actions individuals, communities, and governments can take to mitigate the effects of climate change.
One key aspect to consider when analyzing the impacts of climate change is temperature variation. Rising global temperatures alter weather patterns, leading to more frequent and intense heatwaves, droughts, and wildfires. These events not only endanger human lives but also disrupt ecosystems by causing water scarcity, damaging vegetation, and increasing the risk of forest fires. Additionally, higher temperatures can directly affect species survival and migration patterns, potentially leading to shifts in biodiversity distribution.
Another important factor is precipitation shifts. Climate change can cause alterations in rainfall patterns, including changes in timing, intensity, and distribution. This can result in more frequent and severe floods or prolonged periods of drought, both of which have detrimental consequences for ecosystems and human populations. Floods can destroy habitats and lead to soil erosion, while droughts can reduce water availability for both humans and wildlife.
Rising sea levels are another significant consequence of climate change. As global temperatures rise, glaciers melt and thermal expansion occurs, causing oceans to expand. This poses a serious threat to coastal cities and low-lying areas around the world. Increased flooding due to storm surges threatens infrastructure, displaces communities, destroys habitats like coral reefs and wetlands, and contaminates freshwater sources with saltwater intrusion.
To address these challenges posed by climate change, various mitigation strategies have been proposed at different levels. On an individual level, adopting sustainable practices such as reducing energy consumption, recycling waste materials properly, using public transportation or electric vehicles instead of conventional cars are some steps that can contribute towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
At the community level, initiatives like promoting renewable energy sources (such as solar or wind power), implementing efficient waste management systems (including recycling programs), advocating for sustainable agriculture practices (like organic farming or agroforestry), establishing local conservation projects (to protect biodiversity hotspots), are all important steps towards mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Governments play a crucial role in developing policies and regulations that promote sustainable practices on a larger scale. These can include setting emission reduction targets, investing in renewable energy infrastructure, implementing carbon pricing mechanisms, supporting research and development for clean technologies, and participating in international agreements like the Paris Agreement to collectively address climate change.
In conclusion, climate change is a complex issue with wide-ranging impacts on our environment. Understanding these consequences, such as temperature variations, precipitation shifts, and Rising sea levels is essential for developing effective mitigation strategies. By taking individual actions, fostering community initiatives, and implementing government policies that prioritize sustainability, we can work towards creating a more resilient future for both ecosystems and human societies.
Causes
Climate change is a complex phenomenon that has been attributed to various causes. One example of these causes is the increase in greenhouse gas emissions resulting from human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation. These actions release significant amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere, leading to an enhanced greenhouse effect and subsequent global warming.
To further understand the impact of climate change, it is important to recognize some key factors contributing to its occurrence:
- Industrialization: The rapid growth of industries worldwide has led to increased energy consumption and reliance on fossil fuels. This relentless demand for energy has significantly contributed to the rise in CO2 emissions.
- Land Use Changes: Deforestation plays a crucial role in climate change as trees absorb CO2 through photosynthesis. When forests are cleared or burned, the stored carbon is released back into the atmosphere, exacerbating global warming.
- Agricultural Practices: Certain agricultural practices, like excessive use of synthetic fertilizers and improper management of livestock waste, contribute to nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions – another potent greenhouse gas.
- Waste Management: Improper disposal methods and inefficient waste treatment processes lead to methane (CH4) emissions. Methane is a powerful greenhouse gas with a higher capacity for trapping heat than CO2.
The emotional implications of these causes cannot be overlooked. Climate change threatens our environment and ecosystems, impacting not only nature but also posing risks to human health and well-being. It affects vulnerable communities disproportionately and can lead to economic instability globally.
| Causes | Impact |
|---|---|
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Enhanced greenhouse effect |
| Deforestation | Loss of biodiversity |
| Agricultural Practices | Impaired food security |
| Waste Management | Air pollution |
Recognizing these causative factors enables us to better comprehend the urgency for action against climate change. By understanding how specific human activities contribute to this global challenge, we can develop effective strategies and policies aimed at mitigating its effects.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about “Consequences,” it is vital to explore how these causes manifest in tangible outcomes that directly affect our environment and society. By examining the consequences, we can gain a deeper understanding of the far-reaching impact of climate change.
Consequences
Climate Change in the Environment: The Impact
These actions release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, leading to a range of consequences that significantly impact our environment. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate and adapt to climate change.
One example illustrating the impact of climate change on ecosystems is the bleaching of coral reefs. Rising sea temperatures due to global warming have resulted in widespread coral bleaching events across various regions. For instance, the Great Barrier Reef in Australia has experienced consecutive years of severe bleaching, causing significant damage to this iconic ecosystem. This case study exemplifies how climate change can disrupt delicate ecological balance and threaten biodiversity.
- Increased frequency and intensity of natural disasters such as hurricanes, wildfires, and floods.
- Disruption of agricultural systems, leading to food insecurity for vulnerable populations.
- Loss of habitat for many species, contributing to higher extinction rates.
- Negative impacts on public health through the spread of diseases like malaria and dengue fever.
| Consequences | Environmental Impacts | Social Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme weather events | – Destruction of infrastructure- Flooding – Landslides | – Human displacement- Economic losses |
| Sea-level rise | – Coastal erosion- Inundation of low-lying areas | – Population relocation- Salinization of freshwater sources |
| Melting ice caps | – Habitat loss for Arctic wildlife | – Cultural disruption |
| Ocean acidification | – Coral reef degradation | – Decline in fisheries |
It is evident that climate change poses significant challenges to both the environment and society. To address these issues, the next section will explore mitigation strategies aimed at Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to the changing climate.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about “Mitigation,” we must recognize the urgency of taking action to combat climate change. By implementing effective measures, we can work towards a sustainable future for ourselves and generations to come.
Mitigation
Section H2: Consequences
Having explored the various causes of climate change, it is imperative to delve into its consequential effects on our environment. The impact of climate change reaches far and wide, altering ecosystems, disrupting weather patterns, and endangering countless species.
Consequences:
One example that vividly illustrates the dire consequences of climate change can be seen in the melting Arctic ice. Over the past few decades, rising temperatures have led to a significant reduction in sea ice coverage during summer months. This decline has not only disrupted the delicate balance of marine life but also accelerated global warming as less sunlight is reflected back into space.
To truly comprehend the magnitude of these consequences, one must consider some key aspects affected by climate change:
- Biodiversity loss: As habitats shift due to changing climatic conditions, many plant and animal species struggle to adapt or face extinction.
- Extreme weather events: More frequent and intense hurricanes, droughts, floods, and heatwaves are becoming commonplace worldwide.
- Food security challenges: Disrupted agricultural productivity and shifting growing seasons threaten food supplies for vulnerable communities.
- Health risks: Climate change exacerbates existing health issues such as respiratory diseases while increasing exposure to new infectious diseases like Zika virus.
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Biodiversity Loss | Endangered species |
| Extreme Weather Events | Increased frequency and intensity |
| Food Security Challenges | Decreased agricultural productivity |
| Health Risks | Higher prevalence of diseases |
These profound consequences highlight the urgent need for action. It is crucial that we prioritize mitigation strategies aimed at curbing further damage caused by climate change. By understanding how human activities contribute to environmental degradation, we can strive towards sustainable solutions that protect both our planet’s fragile ecosystems and future generations’ well-being.
Transition sentence into subsequent section about “Renewable Energy”:
In light of the pressing need for change, exploring Renewable Energy Sources presents a promising pathway towards mitigating climate change.
Renewable Energy
Transition from Previous Section:
Having explored various mitigation strategies, it is crucial to understand the importance of transitioning towards renewable energy sources. By harnessing sustainable alternatives, we can mitigate the adverse effects of climate change and ensure a more resilient future for our environment.
Harnessing Renewable Energy Sources
One compelling example that highlights the potential positive impact of renewable energy is the case study of SolarCity in California. This company specializes in installing solar panels on residential properties. Through their efforts, they have significantly reduced carbon emissions by generating clean electricity directly from sunlight, thereby reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
To truly grasp the significance of Adopting Renewable Energy, consider the following emotional bullet points:
- Hope: Embracing renewable energy offers hope for a cleaner and healthier planet.
- Empowerment: Utilizing sustainable alternatives empowers communities to take charge of their own energy needs.
- Resilience: Investing in renewables enhances our ability to withstand environmental challenges and build a more robust society.
- Legacy: Choosing renewable energy today ensures a better tomorrow for generations to come.
Furthermore, let’s visualize some key statistics related to renewable energy through this three-column table:
| Wind Power (in GW) | Solar Power (in GW) | Hydroelectric Power (in GW) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global | 591 | 644 | 1,300 |
| Europe | 192 | 138 | 201 |
| Asia | 217 | 317 | 320 |
| Americas | 130 | 133 | 418 |
These figures demonstrate not only the growing global capacity but also regional variations in embracing different forms of renewable energy. It reinforces how renewable energy sources are gaining momentum worldwide, fostering a transition towards a sustainable future.
In light of the significant benefits and progress made in harnessing renewable energy, it becomes imperative to explore further measures for reducing our carbon footprint. The subsequent section will delve into various strategies that individuals and communities can adopt to contribute actively to combating climate change.
Transition to Next Section:
Moving forward, let us examine effective methods for reducing our carbon footprint and making meaningful contributions towards mitigating the impact of climate change.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
Renewable Energy has emerged as a key solution in mitigating the adverse effects of climate change. By harnessing natural resources such as sunlight, wind, water, and geothermal heat, renewable energy technologies offer an alternative to fossil fuels that is both sustainable and environmentally friendly. The transition towards renewable energy sources not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also promotes economic growth and energy independence.
One noteworthy example showcasing the positive impact of renewable energy is Germany’s Energiewende (Energy Transition) initiative. This comprehensive strategy aims to shift Germany’s energy production from nuclear and fossil fuels to renewables by 2050. Through substantial investments in solar and wind power infrastructure, Germany has significantly increased its share of renewable electricity generation over the past decade. As a result, it has reduced carbon dioxide emissions while creating new jobs and fostering innovation within the clean energy sector.
Transitioning to renewable energy offers several benefits for both society and the environment:
- Reduced carbon footprint: Renewable energy sources produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, minimizing their contribution to global warming.
- Enhanced air quality: Unlike burning fossil fuels which release pollutants into the atmosphere, renewable technologies have minimal air pollution impacts, leading to cleaner air for communities.
- Improved public health: By reducing reliance on coal-fired power plants or other polluting energy sources, renewable energy can help alleviate respiratory illnesses and other health issues associated with poor air quality.
- Increased resilience against climate change: Investing in decentralized renewable systems ensures a more resilient electrical grid capable of withstanding extreme weather events linked to climate change.
Table 1 below highlights the environmental advantages of utilizing different forms of renewable energy:
| Renewable Energy Source | Environmental Advantages |
|---|---|
| Solar Power | No direct greenhouse gas emissions; abundant resource |
| Wind Power | Negligible carbon footprint; inexhaustible resource |
| Hydropower | Clean source of electricity; helps manage water resources |
| Geothermal Energy | Minimal emissions; source of both heat and electricity |
In conclusion, transitioning to renewable energy sources is crucial in mitigating climate change. The example of Germany’s Energiewende initiative demonstrates the positive impact such efforts can have on reducing carbon dioxide emissions while fostering economic growth. By adopting renewable technologies, society can benefit from reduced greenhouse gas emissions, improved air quality, better public health outcomes, and increased resilience against climate-related challenges.
Moving forward, it is imperative to explore Policies and Regulations that facilitate this transition towards a sustainable future. In the subsequent section about “Policies and Regulations,” we will delve into specific measures taken by governments worldwide to promote renewable energy adoption and address the challenges associated with scaling up these technologies.
Policies and Regulations
Reducing Carbon Footprint: A Step Towards Mitigating Climate Change
The impacts of climate change are becoming increasingly evident, with rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and the loss of biodiversity. To combat these challenges, reducing our carbon footprint has emerged as a crucial step towards mitigating climate change. By adopting sustainable practices and making conscious choices in various aspects of our lives, we can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to the preservation of our environment.
One example that highlights the importance of reducing carbon footprint is the case study of XYZ Corporation. This multinational company implemented several measures aimed at minimizing its environmental impact. They introduced energy-efficient technologies in their manufacturing facilities, incentivized employee carpooling initiatives, and transitioned to renewable sources for powering their operations. Through these efforts, XYZ Corporation was able to lower its annual carbon emissions by 30%, not only showing significant progress but also setting an inspiring precedent for other businesses worldwide.
To further emphasize the significance of this issue, consider the following bullet points:
- The transportation sector alone contributes approximately 14% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Household energy consumption accounts for around 25% of total CO2 emissions globally.
- Industrial processes generate nearly one-fourth (24%) of all human-induced greenhouse gases.
- Agriculture and deforestation activities contribute roughly 24% to global greenhouse gas emissions.
These statistics clearly demonstrate how different sectors play a role in contributing to climate change and underscore the urgent need for collective action through reducing our carbon footprint.
| Sector | Contribution to Global Emissions |
|---|---|
| Transportation | 14% |
| Household | 25% |
| Industry | 24% |
| Agriculture | 24% |
As individuals and communities, we have the power to make a difference by implementing simple yet effective actions such as using public transportation or cycling instead of driving cars, opting for energy-efficient appliances and renewable energy sources, supporting sustainable farming practices, and participating in reforestation efforts. By collectively embracing these changes, we can significantly reduce the carbon footprint on our planet.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about “Global Warming Factors,” it is essential to recognize that reducing our carbon footprint contributes not only to mitigating climate change but also addresses other critical aspects of global warming. Understanding these factors will provide a comprehensive perspective on the challenges ahead and guide us towards finding sustainable solutions for a better future.
Global Warming Factors
Climate Change in the Environment: The Impact
Policies and Regulations have played a crucial role in addressing the challenges posed by climate change. However, it is important to understand the various factors contributing to global warming in order to effectively implement these policies. This section will explore some of these factors and their implications on the environment.
To illustrate the impact of climate change, let us consider a hypothetical case study involving a coastal city. Rising sea levels due to global warming pose a significant threat to this city’s infrastructure and population. As temperatures continue to rise, glaciers melt at an accelerated rate, resulting in increased water volume that flows into oceans and seas. Consequently, this leads to higher sea levels which can result in destructive storm surges, floods, and erosion along the coastlines, endangering both human settlements and natural habitats.
The following bullet point list highlights several key consequences of rising global temperatures:
- Increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves.
- Disruption of ecosystems leading to loss of biodiversity.
- Negative impacts on agriculture including reduced crop yields and changes in growing seasons.
- Threats to public health through the spread of diseases and increased respiratory problems due to air pollution.
Furthermore, examining the table below helps visualize how these consequences affect different aspects of our lives:
| Consequences | Impacted Areas | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Weather | Infrastructure | Development of |
| Events | resilient structures | |
| Biodiversity Loss | Natural Habitats | Implementation |
| of conservation | ||
| strategies | ||
| Agriculture | Food Security | Adoption of |
| Challenges | sustainable farming | |
| Public Health | Human Health | |
Understanding the consequences and their associated impacts is crucial in developing effective strategies to mitigate climate change. In the subsequent section, we will delve into the specific effects that climate change has on ecosystems, highlighting the importance of preserving our natural resources for future generations.
Impacts on Ecosystems
The effects of climate change extend far beyond rising global temperatures. One key area where these impacts are evident is in the delicate balance of ecosystems. To illustrate this, let us consider a hypothetical case study involving a coral reef ecosystem.
Coral reefs, known as “the rainforests of the sea,” support an incredible diversity of marine life and provide numerous ecosystem services. However, with increasing ocean temperatures due to global warming, corals become stressed and expel their symbiotic algae, leading to coral bleaching. This process weakens the overall health and resilience of the reef system, making it more susceptible to disease outbreaks and reducing its ability to provide habitat for countless species.
The consequences of such changes in ecosystems go well beyond just one example. Here are some broader impacts that climate change has on various ecosystems:
- Alteration of predator-prey relationships
- Changes in migration patterns
- Disruption of pollination networks
- Shifts in vegetation distribution
These impacts can have profound emotional implications for both humans and other living organisms that depend on healthy ecosystems for survival. Let us now explore these effects further through a table showcasing specific examples:
| Impact | Example | Emotional Response |
|---|---|---|
| Loss of biodiversity | Decline in Amazon rainforest species richness | Concern |
| Food insecurity | Decreased fish populations in Lake Chad | Anxiety |
| Increased wildfires | Devastating fires destroying California forests | Fear |
| Spread of diseases | Expansion of malaria-carrying mosquitoes’ range | Worry |
Understanding the potential repercussions outlined above emphasizes the urgency for action to mitigate climate change’s impact on ecosystems. In light of this necessity, we turn our attention to adaptation strategies that can help minimize these adverse effects while fostering resilience in our natural environment.
Transitioning into the subsequent section on “Adaptation Strategies,” we will explore proactive measures that can be taken to address the challenges posed by climate change and ensure a sustainable future for both ecosystems and human societies.
Adaptation Strategies
Climate change has had a profound impact on ecosystems worldwide, leading to significant changes in biodiversity and ecological processes. For instance, let’s consider the case of the Great Barrier Reef, one of the most iconic and diverse marine ecosystems on our planet. Rising ocean temperatures due to global warming have caused widespread coral bleaching events in recent years, resulting in massive coral die-offs and threatening the long-term survival of this fragile ecosystem.
The impacts of climate change on ecosystems are far-reaching and extend beyond marine environments. Here are some key effects observed across various ecosystems:
- Shifts in species distribution: As temperatures rise, many plant and animal species are forced to migrate or adapt to new habitats that can provide suitable conditions for their survival.
- Changes in phenology: Climate change alters the timing of important biological events such as flowering, migration patterns, and breeding seasons. These disruptions can lead to mismatches between species interactions and affect overall ecosystem functioning.
- Loss of habitat: Rising sea levels, melting glaciers, and more frequent extreme weather events result in habitat loss for numerous species. This loss not only directly affects those organisms but also disrupts entire food webs and ecological relationships.
- Increased risk of invasive species: Climate change creates favorable conditions for non-native species to establish themselves in new areas where they may outcompete native species or introduce diseases that devastate local populations.
These impacts are depicted below using bullet points:
- Shifts in species distribution
- Forced migrations
- Adaptation challenges
- Changes in phenology
- Mismatches between interactions
- Altered reproductive success rates
- Loss of habitat
- Coastal erosion
- Glacier retreat
- Increased risk of invasive species
- Outcompetition of nativespecies
- Disease introduction
Additionally, we present a table highlighting some specific examples illustrating these impacts:
| Impact | Examples |
|---|---|
| Shifts in species distribution | Polar bears moving northward due to melting sea ice |
| Changes in phenology | Earlier flowering of plants in temperate forests |
| Loss of habitat | Coastal erosion leading to nesting site loss for seabirds |
| Increased risk of invasive species | Introduction of non-native fish species into freshwater ecosystems |
In light of these environmental changes, it is crucial that we explore adaptation strategies and develop effective measures to mitigate the impacts. The following section will delve into some key approaches aimed at addressing climate change and reducing its detrimental effects on our planet.
Transitioning smoothly, let’s now turn our attention to alternative energy solutions as a means to combat climate change and create a more sustainable future.
Alternative Energy Solutions
Transition:
Alternative Energy Solutions
One example of an alternative energy solution is the use of solar power. Solar panels are installed on rooftops or in open spaces to harness sunlight and convert it into electricity. This renewable source of energy not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also provides a sustainable and reliable power supply. For instance, a case study conducted in California found that installing solar panels across residential areas resulted in a significant decrease in carbon dioxide emissions by 34% within just one year.
To further emphasize the importance of adopting alternative energy solutions, consider the following bullet points:
- Renewable sources such as wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass can provide cleaner alternatives compared to fossil fuels.
- Implementing these technologies can reduce our dependence on finite resources and combat climate change simultaneously.
- These solutions contribute to job creation and economic growth in industries associated with green technology.
- Embracing alternative energy stimulates innovation and fosters global collaboration towards achieving sustainability goals.
The table below illustrates some key advantages offered by different types of alternative energy sources:
| Energy Source | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Solar Power | Renewable; low maintenance costs |
| Wind Power | Abundant resource; no fuel costs |
| Hydroelectricity | Clean; reliable |
| Biomass | Utilizes organic waste material |
By diversifying our energy mix through the adoption of these sustainable practices, we pave the way for a brighter future that prioritizes environmental preservation while meeting our growing energy needs. This sets the stage for discussion about sustainable practices which will be explored in depth in subsequent sections.
With alternative energy solutions offering promising possibilities for mitigating climate change’s impact, let us now delve into sustainable practices that can further contribute to a greener future.
Sustainable Practices
Alternative Energy Solutions have been explored as a means to mitigate the effects of climate change. However, it is equally important to consider sustainable practices that can further contribute to environmental preservation. By adopting such practices and incorporating them into our daily lives, we can make a positive impact on the environment. This section will discuss some key sustainable practices and their potential benefits.
One example of a sustainable practice is reducing water consumption in households. By installing low-flow faucets and toilets, individuals can significantly decrease their water usage without compromising functionality. For instance, a study conducted by the Environmental Protection Agency found that replacing older toilets with low-flow models could save up to 13,000 gallons of water per year for an average family of four (EPA, 2019). This reduction in water consumption not only conserves this valuable resource but also reduces energy required for pumping and treating water.
To further promote sustainability, recycling initiatives play a crucial role. Recycling materials like paper, plastic, glass, and aluminum helps reduce waste sent to landfills while conserving natural resources. According to research by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), recycling one ton of paper saves around 17 trees and avoids generating greenhouse gas emissions equivalent to taking two cars off the road for one year (EPA, 2020). Additionally, recycling plastics helps minimize pollution caused by their production process and prevents these non-biodegradable materials from ending up in oceans or other ecosystems.
Composting organic waste represents another effective sustainable practice. Food scraps and yard trimmings can be composted instead of being thrown away as garbage. Compost enriches soil quality by providing essential nutrients necessary for plant growth while reducing methane emissions produced in landfills through anaerobic decomposition. Furthermore, utilizing compost enhances soil’s ability to retain moisture, promotes biodiversity within the ecosystem surrounding plants’ root systems – ultimately contributing positively towards maintaining healthy landscapes.
Incorporating these sustainable practices into our daily lives can significantly contribute to preserving the environment. By reducing water consumption, recycling materials, and composting organic waste, we actively take steps towards mitigating climate change and its adverse effects on our planet.
Sustainable Practices
Benefits of sustainable practices:
- Conserves valuable resources
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions
- Minimizes pollution
- Enhances biodiversity
| Practice | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Water conservation | – Reduces water usage- Saves energy |
| Recycling | – Conserves natural resources- Reduces waste |
| Composting | – Enriches soil quality- Decreases methane emissions |
International Cooperation
Climate Change in the Environment: The Impact
Sustainable Practices have proven to be effective in mitigating climate change and reducing its impact on the environment. However, these practices alone are not sufficient to address the global nature of this issue. International cooperation is crucial for implementing comprehensive strategies that can effectively tackle climate change on a larger scale.
One example that highlights the need for international cooperation is the case of Deforestation in the Amazon rainforest. Despite sustainable practices being implemented by some countries within their borders, illegal logging and land encroachment continue to threaten one of the world’s most important carbon sinks. To combat this issue, it requires collaboration among nations to enforce stricter regulations, share resources, and implement joint initiatives aimed at preserving this vital ecosystem.
- Enhanced sharing of scientific research and data across borders
- Collaborative efforts to develop alternative energy sources
- Joint financing mechanisms to support developing countries’ transition towards low-carbon economies
- Creation of an international framework for monitoring and reporting greenhouse gas emissions
These points serve as reminders that tackling climate change necessitates collective action beyond individual country boundaries. By embracing such collaborative approaches, we can foster greater understanding, exchange knowledge and expertise, and collectively work towards achieving long-term environmental sustainability.
Additionally, a three-column table below illustrates how different countries contribute to global greenhouse gas emissions:
| Country | Annual CO2 Emissions (in million metric tons) |
|---|---|
| China | 10,065 |
| United States | 5,414 |
| India | 3,274 |
This table provides a clear visual representation of each country’s contribution to global emissions. It underscores the importance of international cooperation in managing and reducing these emissions collectively rather than focusing solely on individual actions.
In conclusion, sustainable practices play a significant role in combating climate change, but their impact can be limited without international cooperation. By working together to share knowledge, resources, and responsibilities, nations can address this global challenge more effectively. Only through collective action can we ensure a sustainable future for our environment and succeeding generations.