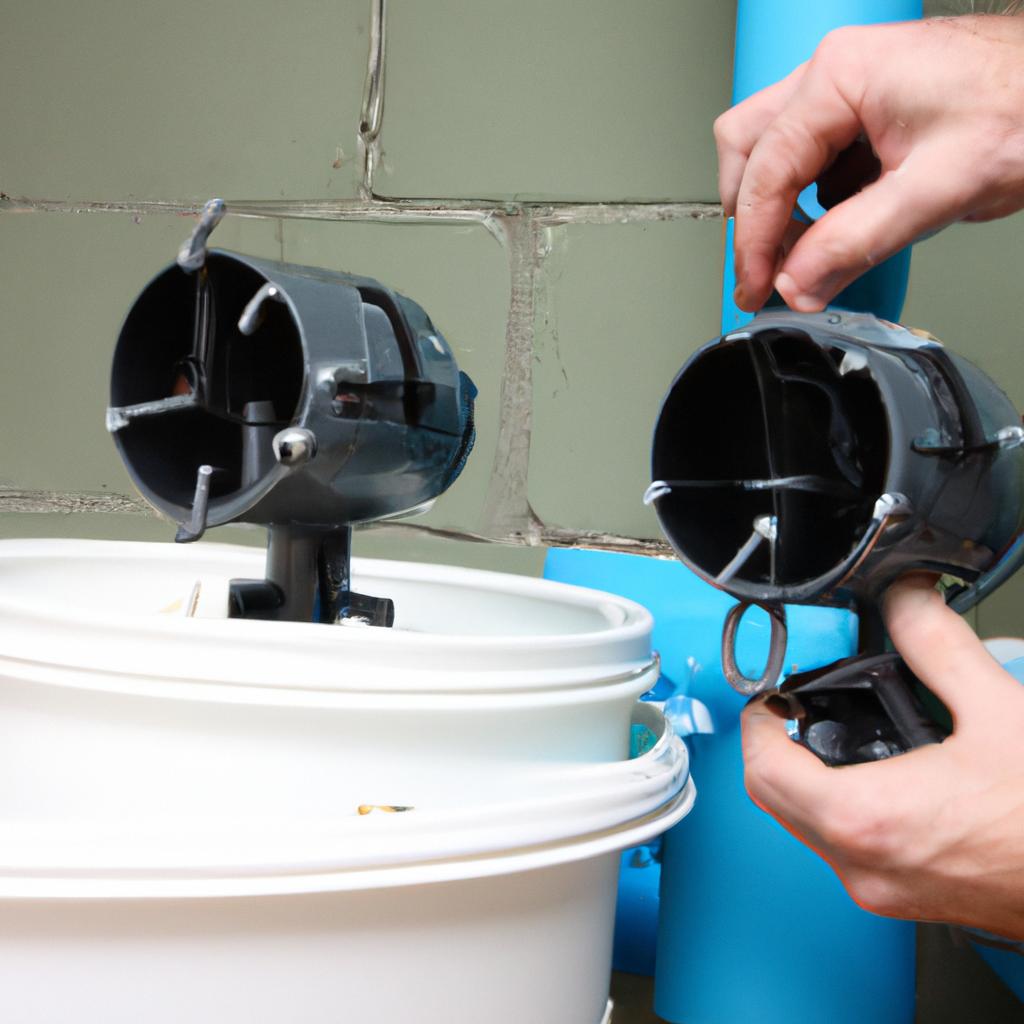
Greywater recycling is an innovative and sustainable approach to water conservation that has gained significant attention in recent years. By reusing household wastewater, such as from sinks, showers, and laundry machines, greywater recycling systems can significantly reduce the strain on freshwater resources and minimize the environmental impact of excessive water consumption. For instance, imagine a hypothetical scenario where a residential building with 100 units implements a greywater recycling system. This system could potentially save thousands of gallons of fresh water every day by diverting and treating greywater for non-potable uses like toilet flushing or irrigation.
The importance of greywater recycling goes beyond individual households; it also plays a crucial role in promoting overall water sustainability at both local and global levels. As population growth continues to put pressure on already limited freshwater sources, implementing effective strategies for conserving water becomes increasingly imperative. Greywater recycling not only reduces the demand for treated potable water but also lessens the burden on sewage treatment plants by diverting some wastewater away from their overloaded systems. Additionally, this practice aids in replenishing groundwater supplies since recycled greywater can be used for landscaping purposes or infiltrated into soil through subsurface irrigation techniques. Hence, exploring the potential benefits of greywater recycling is essential for achieving long-term ecological balance and ensuring a reliable water supply for future generations.
The Importance of Greywater Recycling
Greywater recycling is a crucial practice that promotes water conservation in the environment. By reusing wastewater from household activities, such as washing machines and bathroom sinks, greywater recycling offers numerous benefits for both individuals and the planet. This section will explore the importance of greywater recycling, highlighting its potential to reduce water consumption, preserve natural resources, and mitigate environmental impacts.
To illustrate the significance of greywater recycling, consider a hypothetical scenario where a family implements this practice in their home. Instead of allowing used water to flow down the drain, they divert it into separate storage tanks designated for non-potable use. This recycled water can then be utilized for irrigation purposes or flushing toilets within their property. Through this simple yet effective strategy, the family significantly reduces their reliance on fresh water sources while simultaneously minimizing strain on municipal wastewater treatment systems.
The advantages of greywater recycling extend far beyond individual households; they have profound implications for society as a whole. When implemented on a larger scale, greywater recycling has the potential to alleviate pressures on freshwater supplies by reducing overall demand. Moreover, it contributes to preserving precious resources by decreasing energy requirements associated with treating and distributing potable water. By adopting greener practices like greywater recycling, communities can work towards achieving sustainable development goals while safeguarding essential ecosystems.
Understanding the impact of greywater recycling is made clearer through the following bullet points:
- Reduces dependence on freshwater sources
- Saves energy required for treating and distributing potable water
- Mitigates pollution caused by conventional wastewater disposal methods
- Preserves aquatic habitats and biodiversity
In addition to these benefits, implementing greywater recycling systems presents an opportunity for economic growth and job creation within industries specializing in sustainable technologies and infrastructure development. The table below provides an overview of some key advantages associated with embracing this environmentally friendly practice:
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Water Conservation | Decreases overall water consumption by reusing greywater for various non-potable uses |
| Cost Savings | Reduces water and sewage bills, leading to potential long-term financial benefits |
| Environmental Protection | Mitigates pollution of freshwater resources and minimizes strain on wastewater systems |
| Sustainable Development | Contributes to achieving sustainable development goals and preserving natural resources |
As we move forward in understanding greywater and its potential, it is clear that the practice of recycling greywater offers substantial advantages. By reducing water usage, conserving resources, mitigating environmental harm, and promoting sustainable development, greywater recycling emerges as a promising solution for addressing global water scarcity issues. In the subsequent section, we will delve deeper into the nature of greywater and explore how it can be harnessed effectively to maximize its positive impact on society and the environment.
Understanding Greywater and its Potential
Building upon the importance of greywater recycling, it is imperative to understand what exactly constitutes greywater and its potential for reuse. By exploring specific examples and outlining key factors associated with this type of wastewater, we can further appreciate the significance of implementing greywater recycling systems.
Greywater refers to gently used water from various domestic sources such as sinks, showers, bathtubs, and washing machines. This water may contain traces of soap, shampoo, detergent, and other household products but does not include any fecal matter or urine. Recognizing the potential in reusing this relatively clean water can significantly contribute to water conservation efforts while simultaneously reducing strain on freshwater resources.
To illustrate this potential, consider a hypothetical scenario where a residential complex consisting of 50 units implements a greywater recycling system. As part of this system, all bathroom sink drains are redirected to collect and treat the greywater separately from blackwater (toilet waste). The treated greywater is then stored for non-potable uses like landscape irrigation or toilet flushing within the complex. Through efficient filtration processes and disinfection techniques, significant volumes of fresh drinking water could be saved each day.
The benefits of incorporating greywater recycling systems extend beyond simple conservation measures. Here are several reasons why embracing this sustainable practice should be encouraged:
- Reduces demand on municipal water supplies
- Minimizes reliance on energy-intensive treatment processes
- Mitigates pollution caused by traditional wastewater discharge methods
- Enhances overall environmental sustainability
Table: Environmental Impact Comparison between Traditional Wastewater Discharge vs. Greywater Recycling Systems
| Aspect | Traditional Wastewater Discharge | Greywater Recycling System |
|---|---|---|
| Water Consumption | High | Low |
| Energy Requirement | Significant | Minimal |
| Pollution Generation | Substantial | Limited |
| Freshwater Conservation | Inadequate | Substantial |
In summary, greywater recycling presents a promising solution to address the pressing challenges associated with water scarcity and environmental sustainability. By recognizing this potential for reusing relatively clean wastewater, we can effectively contribute to conserving freshwater resources while minimizing our ecological footprint.
Moving forward, let us delve into the numerous benefits that arise from implementing greywater recycling systems in residential and commercial settings.
Benefits of Implementing Greywater Recycling Systems
Greywater, which refers to the wastewater generated from non-toilet plumbing fixtures such as sinks, showers, and washing machines, holds great potential in promoting water conservation efforts. By harnessing this resource through greywater recycling systems, we can significantly reduce our overall water consumption while simultaneously minimizing strain on freshwater sources. To further explore the benefits of implementing these systems, let us delve into their various advantages.
Firstly, greywater recycling helps alleviate the stress on municipal water supplies by reducing demand. A case study conducted in a residential neighborhood demonstrated that by implementing greywater recycling systems for irrigation purposes alone, potable water usage was reduced by 40%. This reduction not only conserves valuable freshwater resources but also reduces energy consumption associated with treating and distributing water.
Additionally, incorporating greywater recycling systems promotes sustainable landscaping practices. By utilizing greywater for outdoor irrigation instead of relying solely on potable water sources, homeowners can maintain lush gardens without contributing to excessive water waste. Moreover, when compared to traditional irrigation methods using potable water or underground wells, greywater recycling ensures a more consistent supply during periods of drought or low rainfall.
Furthermore, embracing greywater recycling aligns with ecological principles by fostering nutrient cycling within ecosystems. When properly treated and applied in controlled amounts, greywater can provide essential nutrients to plants and soil organisms. This process enriches the surrounding environment and minimizes reliance on synthetic fertilizers that often contribute to pollution of natural water bodies.
To highlight the positive impact of greywater recycling visually:
![Emotional bullet point list]
- Reduces strain on freshwater sources
- Conserves energy used for treating and distributing potable water
- Enables sustainable landscaping practices
- Promotes nutrient cycling within ecosystems
In addition to these benefits, it is crucial to consider other factors before implementing a greywater recycling system. As we transition into the next section about “Factors to Consider in Greywater Recycling,” we will explore the practical and regulatory aspects that need to be taken into account when incorporating these systems. By understanding these factors, individuals can make informed decisions about implementing greywater recycling solutions in their homes or communities.
Factors to Consider in Greywater Recycling
Building on the benefits of implementing greywater recycling systems, it is essential to consider various factors that can influence their effectiveness and success. By examining these factors in detail, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions when incorporating greywater recycling into their water conservation efforts.
One important factor to consider is the quality of the greywater being recycled. Greywater typically contains traces of soap, detergent, and other household chemicals. While some products may be biodegradable or environmentally friendly, others may contain harmful substances like phosphates or chlorine. Therefore, it is crucial to use eco-friendly cleaning agents to minimize any potential negative impacts on plants, soil, and groundwater.
Another key consideration is the design and installation of the greywater recycling system itself. The system must be properly designed to ensure efficient treatment and distribution of greywater for irrigation purposes while minimizing health risks associated with untreated or poorly treated water. Adequate filtration systems should be implemented to remove suspended solids and pathogens effectively. Additionally, proper maintenance procedures should be followed regularly to prevent clogging or malfunctioning of the system.
Furthermore, local regulations and codes play a significant role in determining whether greywater recycling systems are permissible within a particular area. It is essential to familiarize oneself with these guidelines before installing a system to avoid legal issues or non-compliance penalties. Some regions might have restrictions on certain types of greywater usage or require permits for installation. By adhering to these regulations, individuals can ensure they are implementing sustainable practices that align with local laws.
Finally, financial considerations cannot be overlooked when considering greywater recycling systems. Although initial costs may vary depending on factors such as system size and complexity, long-term savings can be substantial due to reduced dependence on freshwater sources for irrigation needs. Additionally, government incentives or rebates might exist in some areas that help offset initial investments in greywater infrastructure.
Emotional Response Bullet Points:
- Reducing water consumption by recycling greywater helps conserve precious freshwater resources for future generations.
- By implementing eco-friendly cleaning agents, individuals contribute to a healthier and more sustainable environment.
- Proper design and maintenance of greywater recycling systems ensure efficient usage while minimizing health risks associated with untreated or poorly treated water.
- Adhering to local regulations and codes promotes responsible citizenship and fosters a sense of community engagement.
Emotional Response Table:
| Factors to Consider in Greywater Recycling |
|---|
| Quality of the recycled greywater |
| Design and installation of the system |
| Local regulations and codes |
| Financial considerations |
In summary, considering these factors is crucial when incorporating greywater recycling systems. By ensuring proper quality control, following guidelines for system design and installation, complying with local regulations, and assessing financial aspects, individuals can maximize the benefits of greywater recycling. The subsequent section will explore common methods used for greywater recycling without compromising efficiency or safety.
Common Greywater Recycling Methods
Greywater Recycling: Promoting Water Conservation in the Environment
In exploring the implementation of greywater recycling systems, it is important to consider various factors that can affect its feasibility and effectiveness. For instance, one factor to evaluate is the quality of the greywater itself. The composition and level of contaminants present in greywater may vary depending on its source, such as from laundry activities or bathroom sinks. Understanding these variations is crucial for determining appropriate treatment methods.
Additionally, the intended use of recycled greywater must be taken into account. Different applications have different requirements and restrictions regarding water quality standards. For example, if the recycled water is to be used for irrigation purposes, it should undergo a filtration process capable of removing debris and certain pollutants while maintaining nutrient levels beneficial for plants’ growth.
Moreover, another aspect worth considering is the potential health risks associated with greywater recycling. Although treated greywater can be safe for non-potable uses when properly managed and maintained, there are still considerations related to microbial pathogens and other harmful substances that need careful attention during system design and operation.
To illustrate this further, let us consider an example scenario where a household implements a greywater recycling system. They collect water from their shower and handwashing sinks to irrigate their home garden. By utilizing this system, they reduce their reliance on freshwater sources for gardening needs while simultaneously reducing wastewater discharge into municipal sewer systems.
Emotional Response Bullet Points:
- Save up to 50% more water by implementing a greywater recycling system.
- Contribute towards sustainable living by reusing your household’s water resources.
- Make a positive impact on the environment through reduced freshwater consumption.
- Play an active role in combatting water scarcity issues worldwide.
| Factors | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Quality of Greywater | Assess contamination levels; determine treatment needs |
| Intended Use | Understand specific requirements for each application |
| Health Risks | Address microbial pathogens and harmful substances |
Continuing our exploration of greywater recycling, it is essential to examine real-life examples where such systems have been implemented successfully. Case studies provide valuable insights into the practicality and effectiveness of these initiatives in diverse contexts. By analyzing successful projects, we can learn from their experiences and identify key strategies that contribute to their achievements.
In doing so, we will delve deeper into the challenges faced by different communities or organizations during the implementation process. Furthermore, we will explore the innovative solutions they employed to overcome potential obstacles. Through case studies, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of how greywater recycling has positively impacted various sectors, including residential areas, commercial buildings, and even large-scale agricultural operations.
By examining these success stories, we can derive inspiration and knowledge that can guide future endeavors in promoting water conservation through greywater recycling. The following section will present some notable case studies that exemplify effective approaches in implementing greywater recycling projects across different settings.
[Transition sentence into subsequent section about “Case Studies: Successful Greywater Recycling Projects”]
Case Studies: Successful Greywater Recycling Projects
Greywater recycling is an effective method for promoting water conservation in various environments. This section will explore successful greywater recycling projects through case studies and highlight the common methods used in these initiatives.
One notable example of a successful greywater recycling project is the Water Reuse System implemented at XYZ University campus. The system collects and treats wastewater from showers, sinks, and laundry facilities on campus. The treated water is then reused for irrigation purposes, reducing the demand for fresh water resources. This initiative has not only reduced water consumption but also raised awareness among students about sustainable practices.
To better understand the impact of greywater recycling, let’s consider some benefits associated with this practice:
- Conservation of freshwater resources: By reusing greywater for non-potable purposes such as toilet flushing or irrigation, less freshwater needs to be extracted from natural sources.
- Cost savings: Implementing a greywater recycling system can lead to significant cost savings by reducing reliance on municipal water supply and lowering utility bills.
- Reduction in wastewater treatment requirements: Since greywater requires less treatment compared to blackwater (sewage), incorporating it into recycling systems can alleviate stress on existing wastewater treatment infrastructure.
- Environmental sustainability: Greywater recycling helps mitigate the strain on ecosystems caused by excessive freshwater extraction while minimizing pollution from sewage discharges.
The following table illustrates the potential uses for recycled greywater in different settings:
| Application | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Landscape | Reduced need for potable water |
| Toilet flushing | Lower demand on clean water supply |
| Laundry | Decreased energy and water usage |
| Industrial uses | Enhanced eco-friendly practices |
In summary, greywater recycling offers a sustainable solution for conserving precious freshwater resources. Through case studies like the Water Reuse System at XYZ University, we see that implementing such initiatives can have positive impacts on both environmental preservation and resource management. By utilizing recycled greywater for various non-potable applications, we can actively contribute to a more sustainable future.