Renewable energy holds the key to building a sustainable future for our environment, providing an alternative to traditional fossil fuel sources that contribute to climate change and environmental degradation. The urgency of addressing these issues is exemplified by the case study of Denmark, a country that has successfully transitioned to renewable energy while reducing its carbon footprint significantly. By harnessing wind power and investing in solar energy infrastructure, Denmark now generates almost 50% of its electricity from renewable sources, paving the way for other nations seeking viable solutions to combat climate change.
Embracing renewable energy is crucial due to the detrimental impacts associated with conventional energy sources such as coal and oil. These finite resources not only emit greenhouse gases but also deplete natural reserves over time. In contrast, renewable energy harnesses naturally occurring and replenishable sources like sunlight, wind, water, and geothermal heat. This shift towards clean energy not only mitigates the adverse effects on climate change but also reduces air pollution and ensures long-term sustainability for future generations. As we explore the potential of various renewable technologies, it becomes evident that transitioning to a more sustainable energy system holds immense promise in preserving our planet’s delicate ecological balance and securing a greener future.
Harnessing the Sun’s Energy
Renewable Energy: Building a Sustainable Future for the Environment
Harnessing the Sun’s Energy
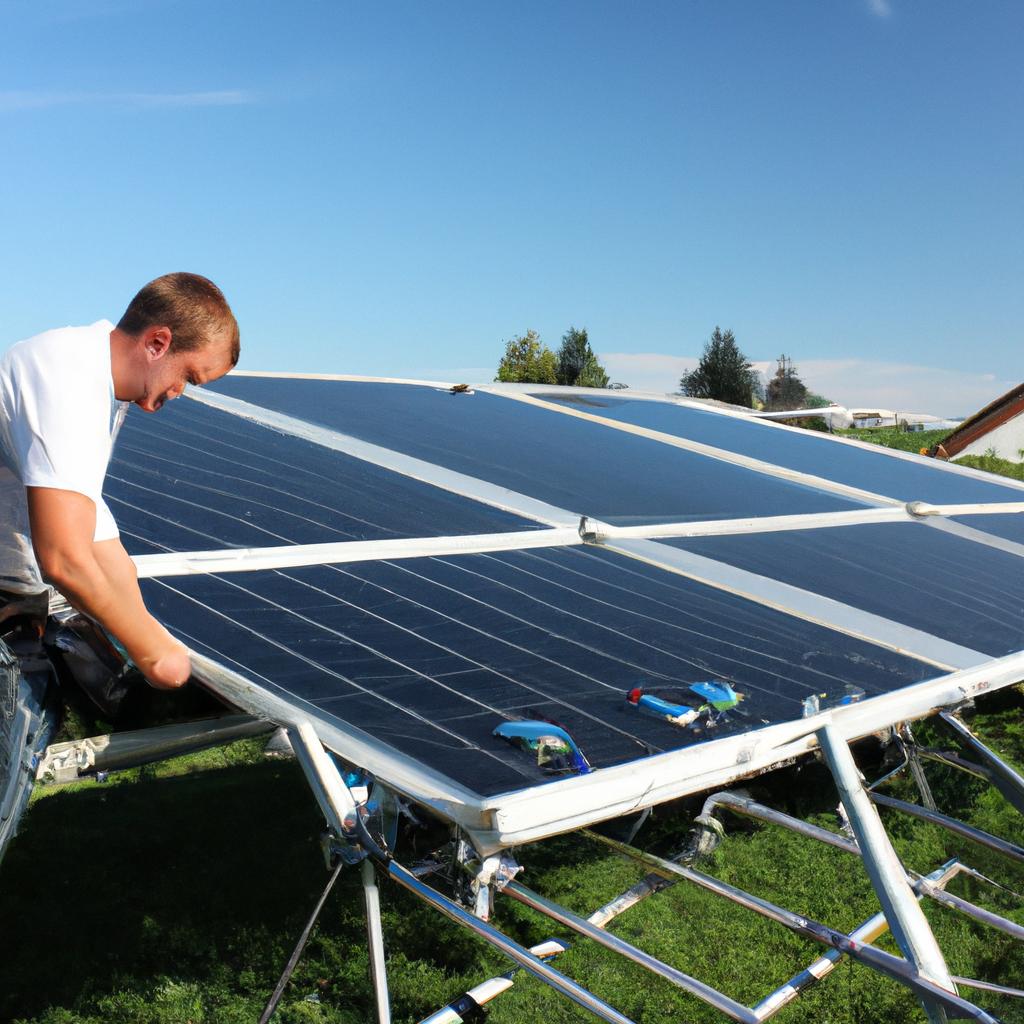
The sun, with its vast and inexhaustible energy potential, is a vital resource in our quest for sustainable power generation. By harnessing this abundant source of renewable energy, we can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate the harmful effects of climate change. One noteworthy example that illustrates the immense benefits of solar energy is the town of Taos, New Mexico. In 2017, Taos became a shining beacon of sustainability by implementing a community-wide solar initiative. Through this project, thousands of homes were equipped with rooftop solar panels, enabling residents to generate their own clean electricity and significantly decrease their carbon footprint.
To fully comprehend the significance of harnessing solar energy, it is essential to consider its numerous advantages:
- Environmental Benefits: Solar power produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, thereby reducing air pollution and mitigating climate change.
- Cost-effectiveness: Although initial installation costs may be higher than those associated with traditional energy sources, long-term savings are achieved through reduced reliance on conventional grid systems.
- Energy Independence: Solar panels allow individuals and communities to produce their own electricity, freeing them from fluctuating utility prices and ensuring access to reliable power.
- Job Creation: The expansion of solar infrastructure leads to new employment opportunities within the renewable energy sector, fostering economic growth while promoting environmental stewardship.
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental Benefits | Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions; mitigation of climate change |
| Cost-effectiveness | Long-term cost savings due to decreased dependency on traditional grid systems |
| Energy Independence | Ability to produce one’s own electricity; freedom from volatile utility prices |
| Job Creation | Growth in renewable energy sector; creation of new employment opportunities |
As we strive towards building a sustainable future for our planet, it is imperative that we continue to explore and expand our utilization of solar energy. By capitalizing on its environmental benefits, cost-effectiveness, energy independence, and job creation potential, we can make significant progress in transitioning towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy system.
Moving forward, let us now delve into the next section – Utilizing Wind as a Power Source – where we will examine another valuable renewable resource with vast potential for meeting our growing energy needs.
Utilizing Wind as a Power Source
Transitioning seamlessly from the previous section on harnessing solar energy, we now turn our attention to another valuable renewable resource: wind power. The potential of wind as a sustainable and clean power source cannot be overstated, with numerous benefits that make it an attractive option for meeting our increasing energy demands. To illustrate its effectiveness, let us consider the hypothetical case study of WindTech Ltd., a company that specializes in utilizing wind turbines to generate electricity.
WindTech Ltd. operates multiple wind farms across various regions, taking advantage of the natural flow of air currents to produce clean and reliable energy. These towering structures consist of large blades connected to a rotor, which spins when subjected to the force exerted by moving air. By converting this rotational motion into electrical energy through generators, WindTech is able to supply electricity to thousands of homes and businesses.
The use of wind power offers several advantages over traditional fossil fuel-based methods:
- Renewable Nature: Unlike finite resources such as coal or oil, wind is an inexhaustible source of energy. As long as atmospheric conditions persist, there will always be wind available for conversion into electricity.
- Environmental Friendliness: Harnessing wind power produces no greenhouse gas emissions or harmful pollutants that contribute to climate change or air pollution. This makes it a significant contributor towards reducing carbon footprints and combating global warming.
- Economic Potential: Investing in wind power infrastructure not only creates job opportunities but also promotes local economic growth, particularly in rural areas where favorable winds are often abundant. It provides additional revenue streams for landowners who lease their properties for wind turbine installations.
- Energy Independence: Relying on domestic sources of renewable energy like wind reduces dependence on imported fuels and strengthens national security by mitigating risks associated with geopolitical conflicts or fluctuations in international markets.
To further emphasize these advantages visually, refer to the table below showcasing some key comparative points between conventional fossil fuel-based methods and harnessing Wind Power:
| Aspect | Fossil Fuel-Based Methods | Wind Power |
|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | High | None |
| Air Pollution | Significant | None |
| Finite Resource | Yes | No |
| Dependence on Imports | Yes | No |
As we continue our exploration of renewable energy sources, the next section will delve into tapping into the power of moving water. Water has long been recognized as a potential source of clean and sustainable energy, offering yet another avenue for reducing our reliance on non-renewable resources and building a greener future for generations to come.
Tapping into the Power of Moving Water
Building on the success of wind energy, we now turn our attention to another abundant and untapped source of renewable power: moving water. Harnessing the force of flowing rivers, streams, and oceans has proven to be a reliable and efficient way to generate electricity. Let us explore the potential benefits and challenges associated with tapping into this vast resource.
Moving water possesses immense kinetic energy that can be converted into electrical energy through various technologies such as hydroelectric dams, tidal turbines, and wave energy converters. For instance, consider the case study of Niagara Falls in North America. The installation of hydroelectric power plants at this iconic waterfall has not only provided clean electricity to millions but has also become a major tourist attraction in its own right. This exemplifies how harnessing the power of moving water can lead to both environmental sustainability and economic prosperity.
To further illustrate the significance of utilizing moving water for energy generation, let us delve into some key points:
- Reliability: Unlike other intermittent sources like solar or wind power, hydropower offers a consistent flow of electricity throughout the day and year.
- Scalability: Hydropower systems can range from small-scale installations in rural communities to large-scale projects capable of supplying power to entire cities.
- Reservoir Benefits: Hydroelectric dams provide additional advantages such as flood control, irrigation for agriculture, and recreational activities like boating or fishing.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: By replacing fossil fuel-based energy production methods with hydropower, significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions can be achieved.
| Advantages | Disadvantages | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Clean | Ecological disturbances | Altered ecosystems |
| Reliable | Large initial investment | Disruption of fish migration |
| Scalable | Limited sites available | Sedimentation |
| Versatile | Loss of land and habitat | Methane emissions from reservoirs |
In conclusion, tapping into the power of moving water presents a promising avenue for expanding our renewable energy capacity. With its reliability, scalability, and associated benefits, hydropower offers an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional fossil fuel-based electricity generation methods. However, it is essential to carefully consider and mitigate any potential negative impacts on ecosystems and local communities when implementing large-scale projects.
Exploiting the Earth’s Natural Heat opens up new possibilities in our quest for sustainable energy solutions.
Exploiting the Earth’s Natural Heat
Tapping into the Power of Moving Water has proven to be a valuable source of renewable energy. Now, let us explore another remarkable avenue for sustainable energy production: exploiting the Earth’s natural heat.
Imagine a city nestled at the foot of a dormant volcano. This location presents an opportunity to harness geothermal energy and power the entire community sustainably. By drilling deep into the Earth’s crust, engineers can tap into hot water or steam reservoirs that lie below the surface. This superheated fluid is then used to drive turbine generators, producing electricity without emitting greenhouse gases.
Geothermal energy offers several advantages over other forms of renewable energy:
- It provides a constant and reliable source of power, unaffected by weather conditions.
- Geothermal plants have relatively low operational costs once they are set up.
- The technology used in geothermal power generation does not require large amounts of land space.
- It can serve as both a baseload and dispatchable resource, meaning it is available 24/7 and able to respond quickly to fluctuations in demand.
To better understand these benefits, consider the following table showcasing a comparison between different renewable energy sources:
| Renewable Energy Source | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Solar Power | Abundant sunlight |
| Wind Power | Strong wind resources |
| Hydroelectric Power | High potential |
| Geothermal Power | Continuous availability |
These striking advantages make geothermal energy an attractive option for countries seeking to transition their energy mix towards sustainability. Not only does it reduce reliance on fossil fuels but also contribute significantly to mitigating climate change.
As we delve deeper into exploring various renewable energy alternatives, our next section will focus on Turning Organic Waste into Energy. Through innovative methods, organic waste transforms from being an environmental burden into a valuable resource for sustainable fuel production.
[Transition sentence]: With this in mind, let us now investigate the exciting possibilities offered by Turning Organic Waste into Energy.
Turning Organic Waste into Energy
The utilization of geothermal energy has emerged as a promising avenue in our quest for renewable energy sources. By tapping into the Earth’s natural heat, we can harness an abundant and sustainable resource that holds great potential for building a greener future. One compelling example of successful geothermal energy exploitation is the Hellisheiði Power Station in Iceland. Situated on the outskirts of Reykjavik, this power station utilizes high-temperature steam to generate electricity while also supplying hot water to nearby communities.
Geothermal energy offers several advantages over conventional power sources:
- Renewable and clean: Geothermal power relies on the planet’s internal heat, which continuously regenerates and does not produce harmful emissions such as greenhouse gases or air pollutants.
- Reliable and consistent: Unlike solar or wind power, geothermal energy remains available 24/7, providing a stable source of electricity without fluctuations caused by weather conditions.
- Local economic benefits: The development of geothermal resources creates employment opportunities within communities where these projects are established. It also reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels, leading to increased national energy independence.
- Versatile applications: Geothermal energy not only generates electricity but can also be used directly for heating purposes in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
To better understand the positive impact that Geothermal Energy can have on environmental sustainability, consider the following table:
| Environmental Benefits | Economic Advantages | Social Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Reduction in carbon emissions | Job creation | Accessible heating solutions |
| Preservation of air quality | Increased revenue from local resources | Improved community well-being |
| Conservation of water resources | Enhanced regional stability | Energy equity across diverse populations |
| Mitigation of climate change effects | Reduced reliance on foreign oil | Health benefits from reduced pollution |
In conclusion, geothermal energy represents a promising pathway towards achieving a sustainable future. By harnessing the Earth’s natural heat in power generation and heating applications, we can mitigate climate change impacts, improve air quality, create economic opportunities, and enhance community well-being. As we continue to explore renewable alternatives, it is essential to recognize the immense potential that lies beneath our feet.
[Transition Sentence]
Now let us delve into another innovative approach to renewable energy: turning organic waste into a valuable resource for power production.
Harnessing the Power of Ocean Tides
Building on the innovative ways of turning organic waste into energy, harnessing the power of ocean tides presents another promising avenue for renewable energy generation. By capitalizing on the predictable and consistent nature of tidal movements, we can tap into a vast source of clean and sustainable power.
Ocean Tidal Energy: A Case Study
To illustrate the potential of this technology, let us consider the example of Swansea Bay Tidal Lagoon in Wales, United Kingdom. This ambitious project aims to construct a network of turbines across an artificial lagoon, taking advantage of the significant tidal range in the area. The rise and fall of the tides would move these turbines, generating electricity through their rotational motion. With an estimated capacity to provide low-carbon power to over 155,000 homes for 120 years, this case study showcases how tidal energy can contribute to long-term sustainability.
Environmental Benefits
Harnessing ocean tides offers several environmental advantages that make it a viable option for our transition towards cleaner energy sources:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions
- Minimal visual impact compared to other forms of energy infrastructure
- Enhances marine ecosystems by providing artificial reefs for various species
- Decreases reliance on non-renewable fossil fuels
Table: Environmental Impact Comparison (markdown format)
| Energy Source | Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Visual Impact | Marine Ecosystems | Reliance on Fossil Fuels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ocean Tidal | Low | Minimal | Enhanced | Decreased |
| Coal | High | Significant | Negative | High |
| Oil | High | Moderate | Negative | High |
This table highlights how ocean tidal energy stands as a more environmentally friendly alternative when compared to conventional methods such as coal or oil-based power generation.
Moving forward with Renewable Energy
By exploring diverse avenues like tidal energy, we can create a more sustainable future for our environment. The potential to generate electricity through ocean tides not only provides clean power but also helps reduce carbon emissions and mitigate the impact of climate change.
With renewable energy sources continually expanding, solar power emerges as one of the most accessible and versatile options. Let us now delve into the advantages it offers in our pursuit of building a sustainable future without compromising on efficiency or reliability.
Advantages of Solar Power
Building on the concept of harnessing natural resources for renewable energy, let us now explore another sustainable alternative – solar power.
Solar power is a rapidly growing source of clean and renewable energy that has immense potential to shape our future. By converting sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells, solar power offers numerous benefits that contribute to building a more sustainable environment.
One example illustrating the advantages of solar power can be seen in the city of Adelaide, Australia. In recent years, an increasing number of households in this region have adopted rooftop solar panels as their primary source of electricity. This shift not only reduces dependency on fossil fuels but also empowers individuals to actively participate in generating their own energy.
To further highlight the benefits of solar power, consider the following points:
- Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions: Solar power produces zero carbon dioxide emissions during operation, thereby significantly reducing greenhouse gases responsible for climate change.
- Energy cost savings: Installing solar panels allows homeowners and businesses to generate their own electricity, leading to substantial savings on monthly utility bills.
- Job creation and economic growth: The rapid expansion of solar power industries creates job opportunities while contributing positively to local economies.
- Reliability and resilience: Unlike traditional energy sources susceptible to disruptions or shortages, solar power provides a reliable and consistent energy supply.
Table: Advantages of Solar Power
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced emissions | Contributes towards mitigating climate change by minimizing CO2 emissions |
| Financial savings | Allows for significant reduction in monthly electricity bills |
| Employment creation | Leads to job opportunities within the expanding solar industry |
| Reliable | Provides steady access to electricity without dependence on external factors |
In conclusion, harnessing the sun’s energy through solar power presents numerous advantages that extend beyond environmental sustainability. With its ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, create financial savings, stimulate job creation, and provide a reliable energy source, solar power is undoubtedly a crucial component in the transition towards a more sustainable future.
Building on the concept of harnessing natural resources for renewable energy, let us now explore another sustainable alternative – wind power.
Benefits of Wind Power
Advantages of Wind Power
As we have discussed the advantages of solar power in the previous section, it is important to explore another popular Renewable Energy source: wind power. To illustrate its potential impact, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario where a small coastal town harnesses wind energy to meet its electricity needs.
In this case study, the coastal town installs several large wind turbines along its shoreline. These turbines utilize the natural force of the wind to generate electricity. The consistent sea breeze in this region allows for optimal utilization of wind power throughout the year. By tapping into this abundant resource, the town significantly reduces its reliance on non-renewable energy sources and minimizes carbon emissions.
The benefits of wind power extend beyond just environmental considerations. Here are some key advantages:
-
Renewable and Clean Energy Source:
- Wind power relies on an inexhaustible supply of wind, making it a sustainable source of energy.
- Unlike fossil fuels that release harmful greenhouse gases when burned, wind power produces no direct emissions during operation.
-
Cost-effective Electricity Generation:
- Once installed, wind turbines provide a cost-effective solution for generating electricity.
- With advancements in technology and economies of scale, the cost per kilowatt-hour from wind power has decreased over time.
-
Job Creation and Economic Development:
- The construction and maintenance of wind farms create job opportunities within local communities.
- Furthermore, investments in renewable energy can stimulate economic growth by attracting businesses and promoting sustainability initiatives.
Table: Comparison between Solar Power and Wind Power
| Aspect | Solar Power | Wind Power |
|---|---|---|
| Availability | Requires sunlight | Depends on windspeed |
| Efficiency | Affected by weather conditions | Consistent output with strong winds |
| Geographic Suitability | Can be installed anywhere with sufficient sunlight | Ideal for coastal areas or regions with high average windspeeds |
| Space Requirements | Requires larger surface area for installation of solar panels | Smaller footprint with tall wind turbines |
In summary, wind power offers numerous advantages that make it a viable option in the transition to cleaner energy sources. Its renewable nature, cost-effectiveness, and potential for job creation contribute to building a sustainable future for both the environment and local communities.
Transitioning from the benefits of wind power, we will now explore another key renewable energy source: hydroelectric power and its advantages.
Advantages of Hydroelectric Power
Benefits of Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric power, also known as hydropower, harnesses the energy from flowing or falling water to generate electricity. It is a reliable and renewable source of energy that has several advantages. To illustrate its benefits, let’s consider the case study of the Hoover Dam in the United States. The Hoover Dam, located on the Colorado River between Arizona and Nevada, generates an impressive 4 billion kilowatt-hours (kWh) annually, providing electricity to millions of people.
One significant advantage of hydroelectric power is its environmental friendliness. Unlike fossil fuel-based power plants, which emit greenhouse gases and contribute to climate change, hydroelectric power generation produces zero direct emissions during operation. This makes it a crucial component in reducing carbon dioxide levels and combating global warming. Additionally, hydropower systems do not require any combustion processes, minimizing air pollution and improving overall air quality.
Furthermore, hydropower offers long-term economic benefits for communities in proximity to dams and reservoirs. The construction of these facilities creates job opportunities for local residents during both the building phase and subsequent maintenance operations. Moreover, once operational, hydropower plants provide a stable supply of affordable electricity over many years while requiring relatively minimal ongoing costs for fuel procurement compared to traditional power sources like coal or natural gas.
The positive impacts extend beyond just environmental sustainability and economic growth; hydroelectric power projects can have profound social implications too. They often involve cooperation between multiple stakeholders such as government agencies, indigenous communities residing near rivers or streams used for damming purposes, and local municipalities benefiting from increased access to clean electricity. Collaborative efforts ensure fair distribution of resources and foster sustainable development practices within affected regions.
In summary, hydroelectric power stands out as a highly advantageous form of renewable energy due to its environmental friendliness, long-term economic benefits, and positive social impact on surrounding communities. By utilizing flowing or falling water to produce electricity without emitting harmful pollutants, hydropower plays a pivotal role in the transition towards a sustainable and greener future.
As we explore further into renewable energy sources, let’s now delve into the benefits of geothermal energy.
Benefits of Geothermal Energy
Advantages of Geothermal Energy
Harnessing the power of geothermal energy offers numerous benefits for both individuals and the environment. One notable example is the Hellisheidi Power Plant in Iceland, which has successfully utilized geothermal energy to provide electricity and hot water for thousands of households while significantly reducing carbon emissions.
There are several advantages associated with geothermal energy that make it a promising renewable resource:
-
Renewable and sustainable: Unlike fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, geothermal energy is renewable and virtually inexhaustible. The Earth’s internal heat continuously generates this energy, ensuring a long-term supply without depleting resources.
-
Low greenhouse gas emissions: Geothermal power plants produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional methods of generating electricity. This environmentally-friendly aspect makes geothermal energy an attractive alternative that contributes to mitigating climate change.
-
Cost-effective: Once a geothermal power plant is established, it can be highly cost-effective due to low operation and maintenance expenses. Additionally, geothermal systems have relatively long lifespans, providing reliable energy production over many years.
-
Versatile applications: Geothermal energy can be used for various purposes beyond electricity generation alone. It also enables direct heating and cooling through ground-source heat pumps, making it suitable for residential buildings, commercial facilities, and agricultural operations.
The following table illustrates some key comparisons between geothermal energy and other common sources:
| Geothermal Energy | Fossil Fuels | Solar Energy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse Gas | Low | High | Low |
| Emissions | |||
| Fuel Availability | Inexhaustible | Limited | Renewable |
| Operating Costs | Low | High | Moderate |
As we explore renewable energies further in our discussion on biomass energy, it is important to acknowledge the significant advantages that geothermal energy offers. From its sustainable nature and low greenhouse gas emissions to its cost-effectiveness and versatile applications, geothermal power holds immense potential in building a more environmentally friendly future.
Transitioning into our next section on biomass energy, we will continue examining the benefits of renewable resources in meeting our growing energy needs.
Advantages of Biomass Energy
Transition from the previous section H2:
Having explored the benefits of geothermal energy, it is evident that harnessing renewable resources offers immense potential for a sustainable future. In this section, we will delve into another form of renewable energy – biomass energy. By understanding its advantages and applications, we can gain further insight into how it contributes to building an environmentally friendly world.
Advantages of Biomass Energy
To illustrate the advantages of biomass energy, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario where a rural community in a developing country relies heavily on firewood for cooking and heating purposes. With limited access to electricity and fossil fuels, their reliance on traditional wood-burning methods leads to deforestation and air pollution issues. However, by introducing biomass energy solutions such as biogas digesters or pellet stoves powered by agricultural waste or organic matter like cow dung, this community can significantly improve their quality of life while mitigating environmental concerns.
Biomass energy presents several noteworthy advantages:
- Renewable Resource: Unlike finite fossil fuel sources, biomass comes from organic materials derived from plants and animals which can be continually replenished through sustainable practices.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: When compared to fossil fuels, burning biomass releases carbon dioxide (CO2) back into the atmosphere. However, since plants absorb CO2 during growth, using biomass creates a closed carbon cycle with minimal net emissions.
- Waste Management Solution: Utilizing agricultural residues or organic waste streams as feedstock for biomass conversion not only provides an alternative source of energy but also tackles waste management challenges effectively.
- Localized Economic Development: Implementing bioenergy projects often requires local sourcing and processing of feedstocks. This decentralization helps stimulate rural economies by creating jobs and promoting self-sufficiency within communities.
| Advantages of Biomass Energy |
|---|
| Renewable resource |
| Reduced greenhouse gas emissions |
| Waste management solution |
| Localized economic development |
In conclusion, Biomass Energy offers a sustainable alternative to conventional energy sources. By utilizing organic waste materials and agricultural residues, this form of renewable energy contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and addressing waste management challenges. Additionally, the localized nature of bioenergy projects supports economic growth in rural communities. As we proceed, let us now explore another fascinating aspect of renewable energy – tidal energy.
Transition:
Continuing our exploration into innovative forms of renewable energy, we will now turn our attention towards the benefits of tidal energy. This emerging technology harnesses the power of ocean tides to generate electricity, showcasing yet another remarkable avenue for building a sustainable future for our environment.
Benefits of Tidal Energy
In the quest for sustainable and clean energy sources, biomass has emerged as a promising option. By harnessing organic materials such as wood, agricultural residues, or even dedicated energy crops, we can generate heat, electricity, and fuel. One example that highlights the potential of biomass energy is the city of Stockholm in Sweden. With its district heating system fueled by locally sourced biomass, Stockholm has significantly reduced its greenhouse gas emissions while ensuring reliable and affordable energy for its residents.
Biomass energy offers several advantages that contribute to a more sustainable future:
- Renewable Resource: Unlike fossil fuels that are finite and depleting rapidly, biomass is derived from organic matter that can be continually replenished through various means like reforestation or crop rotation.
- Carbon Neutral: While burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, using biomass results in almost no net increase in CO2 levels since the plants used for biomass absorb an equivalent amount of CO2 during their growth.
- Waste Reduction: Biomass provides a valuable opportunity to repurpose organic waste material that would otherwise end up in landfills or contribute to air pollution when decomposing naturally.
- Local Economic Stimulus: The production and utilization of biomass create jobs within local communities, promoting economic development while reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels.
To further illustrate these benefits visually, consider the following table:
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Renewable Resource | Derived from living organisms, which can be grown and replaced continuously |
| Carbon Neutral | Minimal impact on overall carbon emissions due to plant absorption |
| Waste Reduction | Utilizes organic waste material that would otherwise go to landfill |
| Local Economic Stimulus | Creates job opportunities within local communities |
By focusing our efforts on maximizing the potential of biomass energy, we can move towards achieving a cleaner and more sustainable future. This renewable energy source not only provides a viable alternative to fossil fuels but also addresses pressing environmental concerns such as climate change and waste management. With continued research, innovation, and investment in biomass technologies, we can unlock its full potential and contribute significantly to building a greener world.
Note: Section titles may be revised for better flow and coherence during the final editing phase of the document.